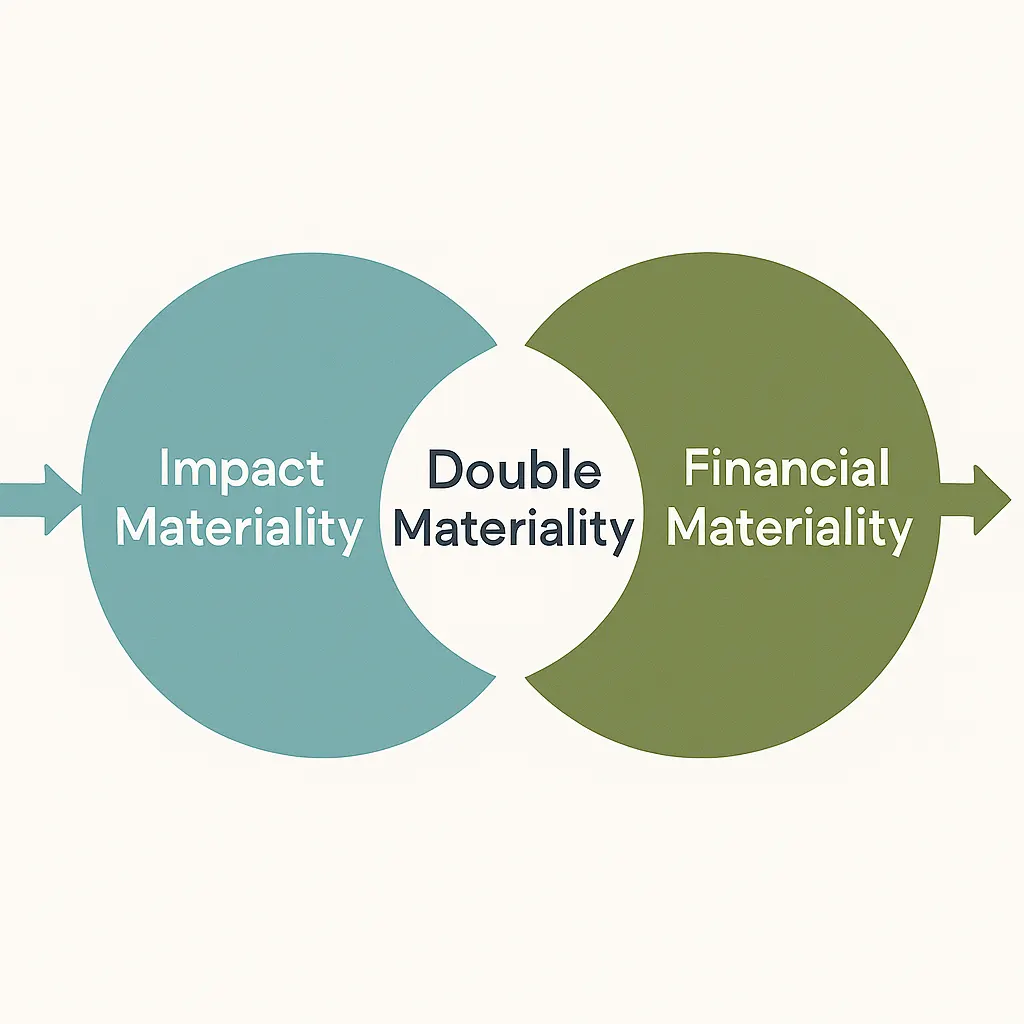
Sustainability reporting is rapidly evolving under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). At its core lies the principle of double materiality, which is a requirement for companies to understand not only how sustainability issues affect their business, but also how their business affects people and the planet.
For many organizations, this can feel complex and time-consuming. That’s where ExecutESG’s Double Materiality Assessment (DMA) service brings clarity. Designed to align with the latest CSRD and ESRS requirements, ExecutESG simplifies every stage of the assessment, from stakeholder input to matrix visualization, which helps companies turn regulatory demands into strategic insight.
Call, visit, send an email or fill out the form – and we will contact you soon to map your company’s situation.
Phone: 040 747 1793
Address: Lapinlahdenkatu 16, 00180 Helsinki
E-mail: [email protected]
What Is Double Materiality?
Materiality has always been central to ESG reporting. Traditionally, companies focused on understanding how environmental or social issues might influence financial performance, for example, how rising energy costs or climate-related risks could impact business results. This is known as financial materiality.
Europe’s updated sustainability regulations expand this view. Companies are now expected to evaluate how their own activities influence society and the environment. This “inside-out” perspective captures a company’s positive and negative impacts, ranging from emissions and resource use to human rights, labor practices, and community impacts.
Together, these two perspectives form double materiality, now the foundation of CSRD reporting.
Difference Between Single and Double Materiality
Single materiality focuses solely on the outside-in perspective, such as how external sustainability issues affect financial performance. Double materiality adds the inside-out perspective, examining how corporate actions affect people and the environment.
This dual lens provides a fuller picture of a company’s sustainability footprint and its interconnected risks and opportunities. It also reinforces the idea that business success is increasingly tied to environmental and social outcomes.
Why Double Materiality Matters for Businesses
Beyond regulatory compliance, double materiality helps organizations build stronger, more resilient strategies. Understanding both financial exposure and societal impact enables companies to identify priority issues, anticipate risks, strengthen stakeholder trust, and embed sustainability into long-term planning.
It becomes not just an obligation, but a strategic tool for growth, credibility, and informed decision-making.
Double Materiality and CSRD Compliance
The CSRD marks a significant step forward in corporate transparency across Europe. It requires companies to disclose detailed, standardized sustainability information alongside financial results.
At the center of this obligation is the Double Materiality Assessment. Without a robust DMA, a CSRD report cannot be considered complete or compliant. The assessment determines which ESG topics must be reported by evaluating both their impact on society and their financial relevance for the company.
The Link Between CSRD and ESRS Reporting Standards
To support CSRD implementation, the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) define what companies must disclose and how information must be structured. Every ESRS topic, including climate, biodiversity, workers, communities, and governance, which must be reviewed through the double materiality lens.
ExecutESG’s DMA framework is built fully in line with ESRS requirements. It guides companies in assessing and prioritizing impacts, risks, and opportunities (IROs) in a consistent, audit-ready format that meets regulatory expectations.
Which Companies Are Required to Perform a Double Materiality Assessment
Under the ongoing CSRD “Omnibus” deregulation adjustments (as of November 24, 2025), the expectation is that large EU companies meeting thresholds of more than 1,000 employees and €450 million in revenue will be mandated to perform a DMA.
However, smaller enterprises are strongly encouraged to perform a simplified DMA — particularly those operating within the value chains of larger companies. ExecutESG supports SMEs with lightweight, scalable DMA tools designed to meet their needs efficiently.

How to Conduct a Double Materiality Assessment
| Step | Stage Title | Brief Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Step1 | Identify and Score Impacts | Collect stakeholder input and assess positive and negative impacts across the value chain aligned with ESRS |
| Step2 | Identify and Score Financial Risks & Opportunities | Evaluate sustainability-related risks and opportunities affecting financial performance using structured scoring |
| Step3 | Determine Material IROs and Topics | Identify material Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities (IROs) and elevate related sustainability topics based on data |
| Step4 | Build the Double Materiality Matrix | Visualize impact and financial materiality in a dynamic matrix with filtering and export options |
| Step5 | Enable Sustainability Action Planning | Use material IROs as the foundation for sustainability actions, budgeting, and prioritization |
Step 1 – Gather and Rate Insights on Impacts
Modern DMA begins with human insight and understanding the real positive and negative impacts a company creates across its operations and value chain. ExecutESG helps organizations centralize stakeholder input and map these impacts clearly against the ESRS framework, establishing a strong evidence base before financial considerations are added.
Step 2 – Gather and Rate Insights on Financial Risks and Opportunities
After impacts are understood, companies evaluate how related risks and opportunities might influence financial performance. ExecutESG streamlines this by guiding users through structured, repeatable rating flows. What is traditionally a spreadsheet-heavy task becomes intuitive and accessible, even for teams without ESG expertise.
Step 3 – Determine Material Impacts, Risks, Opportunities, and Sustainability Topics
Once impacts, risks, and opportunities (IROs) are scored, the system supports facilitated materiality decision-making. Material IROs automatically elevate their associated sustainability topics, ensuring that topic selection is based on real data rather than subjective judgment.
Step 4 – Build and Visualize the Double Materiality Matrix and IRO Plottings
ExecutESG generates a dynamic double materiality matrix, plotting financial and impact significance side-by-side. Users can view results by stakeholder group, filter themes, and export visuals instantly. The tool also enables separate impact and risk visualizations, improving strategic interpretation across teams.
Step 5 – Input Is Ready for Sustainability Action Planning
Once the material IRO list is finalized, it becomes the backbone of sustainability action planning, budgeting, and prioritization. ExecutESG helps companies move smoothly from data to decisions without needing external consulting support.
Benefits and Strategic Impact
ExecutESG’s DMA process turns raw information into strategic clarity. By linking actual impacts with financial implications, companies gain a clear view of where to act, how to manage risks, and how sustainability connects with long-term value creation. This avoids the overcomplicated, consultant-driven approach and empowers teams to take ownership of the process.
Turning Insights Into Business Value and Compliance Readiness
Because ExecutESG integrates data collection, analysis, and visualization, organizations can quickly translate findings into real action. Dashboards and automated reports make it easy for leadership teams to understand how sustainability performance influences business success and ensure CSRD disclosures are complete, accurate, and audit-ready.

Common Challenges and Best Practices
| Area of Concern | Common Pitfalls & Challenges |
| Process Quality | Treating DMA as a mere “box-ticking” exercise, inconsistent documentation, and unclear scoring criteria. |
| Data & Engagement | Weak stakeholder engagement and disorganized, manual data collection processes. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Struggles to keep up with evolving ESRS standards, leading to outdated assessments. |
Typical Pitfalls in Conducting DMA
Organizations often struggle when they treat DMA as a box-ticking exercise or rely on inconsistent documentation. Unclear scoring criteria and weak stakeholder engagement also hinder accuracy. ExecutESG reduces these challenges with guided workflows and built-in validation checks that uphold ESRS and audit standards.
Tips for Efficient Data Collection and Stakeholder Engagement
Early preparation makes a significant difference. Using technology to automate collection, encouraging transparent dialogue about sustainability priorities, and involving diverse teams, from finance to operations, that ensures alignment and stronger outcomes.
Maintaining Alignment With Evolving ESRS Updates
Because sustainability regulations evolve, DMA processes must stay flexible. ExecutESG continuously updates its platform to reflect the latest ESRS guidance, helping companies remain compliant without redoing assessments from scratch.
Summary and Next Steps
A Double Materiality Assessment is more than a reporting requirement, it is the starting point of a forward-looking, responsible, and resilient business strategy.
ExecutESG brings together CSRD-aligned methodology, intelligent analysis tools, and interactive visualizations to help organizations move confidently from compliance to action.
Next steps:
- Launch your DMA with ExecutESG’s guided platform
- Transform your sustainability data into strategic value
- Build transparency and trust across your organization
FAQs
What are the key steps in performing a double materiality assessment under CSRD?
Identify and rate impacts, identify and rate risks and opportunities, engage stakeholders, build a materiality matrix, and make decisions on material IROs, ideally through a platform like ExecutESG’s DMA service.
How does a double materiality matrix differ from a traditional one?
Traditional matrices focus on financial relevance; double materiality matrices include both financial and impact perspectives.
What data sources are used in a double materiality assessment?
Internal business data, stakeholder feedback, performance metrics, and external ESG benchmarks.
How often should companies update their DMA?
Every 1–2 years or when major business or regulatory changes occur.
What are the main challenges companies face in applying double materiality?
Limited data, stakeholder fatigue, and evolving reporting standards.
How do auditors evaluate DMA quality?
They check topic selection, stakeholder documentation, scoring consistency, and ESRS alignment.
What role does stakeholder engagement play?
It ensures balance and credibility, making results both legitimate and actionable.
Can SMEs use simplified DMA approaches?
Yes. ExecutESG provides SME-friendly templates and workflows for scalable implementation.
How do ESG software tools support DMA?
They automate data collection, help engage stakeholder groups, ensure consistency, and produce audit-ready outputs.
What are examples of companies implementing DMA successfully?
Many leading organizations now use structured DMA processes, such as with ExecutESG’s platform that helps them achieve efficient, compliant, and insightful results.
